Adsorption of PFAS onto DES
Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a diverse class of synthetic fluorinated organic substances that have been used in numerous industrial and commercial applications since the 1950s. Due to the extensive utilization of PFAS and subsequent release into the environment, a wide variety of these substances have been identified in air, water, and even breast milk. In addition, most PFAS are resistant to conventional water treatment methods and can escape filtration/adsorption techniques. To address this problem, Dr. Reza’s group has developed several hydrophobic DES, which enable water-based separations.115-120 Aiming to perform a rational selection of the most suitable DES to extract PFAS […]
DES Deconstruction of Sweet Potato Vines to Separate Lignin
Separating lignin from cellulose in biomass is a necessary pretreatment step prior to converting them to biofuels or bioproducts. If byproducts from food production can be separated in an ecofriendly solvent at low pressures, biomass specifically grown for biorefining will not need to be shipped long distances. Thus, this project will allow participants to gain knowledge in the upconversion of agricultural byproducts using DES and the importance of improving the properties of materials such as asphalt and cement.103, 104 Specifically, participants interested in this project will investigate the use of choline chloride–based DES for separating out lignin from sweet potato […]
DES for the Extraction of Contaminants
GUMBOS are solid-phase organic salts with melting points ranging from 25°C to 250°C that are particularly valuable in multiple aspects of the analytical workflow. For example, the hydrophobicity of GUMBOS can be adjusted by modifying the counterion or by incorporating nanomaterials through a simple reprecipitation method in water. Participants involved in this project will develop GUMBOS with magnetic properties and apply them for the extraction and subsequent analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) from environmental samples. The goal is to reduce the need for large volumes of solvents while effectively extracting these organic contaminants from water samples. By leveraging the unique […]
Activity of NADES at the Multiomic Level
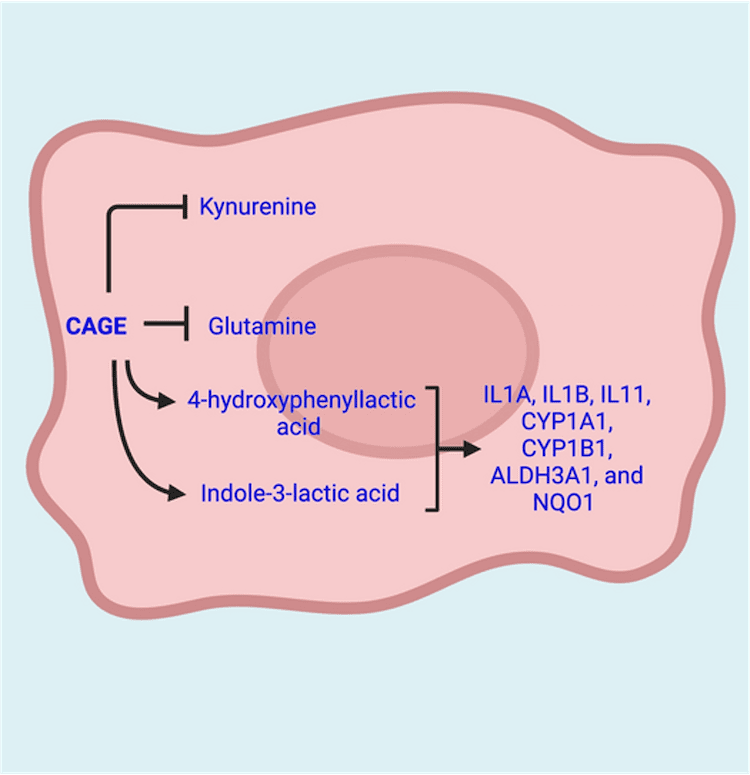
Due to improved biocompatibility, natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) are increasingly explored in biomedicine.93 Yet, our understanding of how they interact with biomolecules at multiomic levels- metabolome, proteome, epigenome, and transcriptome – remains poor. Recently, Agatemor’s group found that a NADES designed from choline and geranic acid (CAGE) upregulates indole-3-lactic acid and 4-hydroxyphenyllactic acid at the metabolomic level, resulting in ligand-independent activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor to signal the transcription of genes at the transcriptomic level.92 Such metabolic-transcriptomic biochemical crosstalk has important implications for metabolic regulation/engineering of inflammation, immune response, cell reprogramming, and chemical detoxification.94 This finding prompted new questions […]