Inhibition of Steroid Sulfatase with 4-Substituted Estrone and Estradiol Derivatives
3. Inhibition of Steroid Sulfatase with 4-Substituted Estrone and Estradiol Derivatives
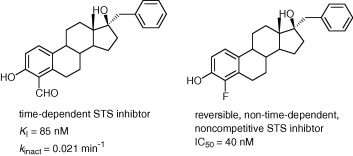
Steroid sulfatase (STS) catalyzes the desulfation of biologically inactive sulfated steroids to yield biologically active desulfated steroids and is currently being examined as a target for therapeutic intervention for the treatment of breast cancer. We previously demonstrated that 4-formyl estrone is a time- and concentration-dependent inhibitor of STS. We have prepared a series of 4-formylated estrogens and examined them as irreversible STS inhibitors. Introducing a formyl, bromo or nitro group at the 2-position of 4-formylestrone resulted in loss of concentration and time-dependent inhibition and a considerable decrease in binding affinity. An estradiol derivative bearing a formyl group at the 4-position and a benzyl group at the 17β-position yielded a potent concentration and time-dependent STS inhibitor with a K(I) of 85 nM and a k(inact) of 0.021 min(-1) (k(inact)/K(I) of 2.3 × 10(5)M(-1)min(-1)). Studies with estrone or estradiol substituted at the 4-position with groups other than a formyl group revealed that good reversible inhibitors can be obtained by introducing small electron withdrawing groups at this position. An estradiol derivative with fluorine at the 4-position and a benzyl group at the 17β-position yielded a potent, reversible inhibitor of STS with an IC(50) of 40 nM. The introduction of relatively small electron withdrawing groups at the 4-position of estrogens and their derivatives may prove to be a general approach to enhancing the potency of estrogen-derived STS inhibitors.
Download PDF »
View on PubMed »
Phan, C.-M.; Liu, Y.; Kim, B.; Mostafa, Y.; Taylor, S. D. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 5999–6005.